Solar Photovoltaic
Definition^1: "Solar cells, also called photovoltaic cells, convert sunlight directly into electricity. Photovoltaics (often shortened as PV) gets its name from the process of converting light (photons) to electricity (voltage), which is called the photovoltaic effect. This phenomenon was first exploited in 1954 by scientists at Bell Laboratories who created a working solar cell made from silicon that generated an electric current when exposed to sunlight. Solar cells were soon being used to power space satellites and smaller items such as calculators and watches. Today, electricity from solar cells has become cost competitive in many regions and photovoltaic systems are being deployed at large scales to help power the electric grid."
The maximum possible energy output of a given installation assumes its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The actual energy output during that period and the capacity factor vary greatly depending on a range of factors, for renewable energy the main factor being the weather conditions. For solar PV it is then important to take into account the $capacity factor$ defined as "the ratio of the net electricity generated, for the time considered, to the energy that could have been generated at continuous full-power operation during the same period"^2.
Data
To generate the data for this model we used International Energy Agency (IEA)^3 and International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)^4 reports.
Some insight on Solar PV evolution
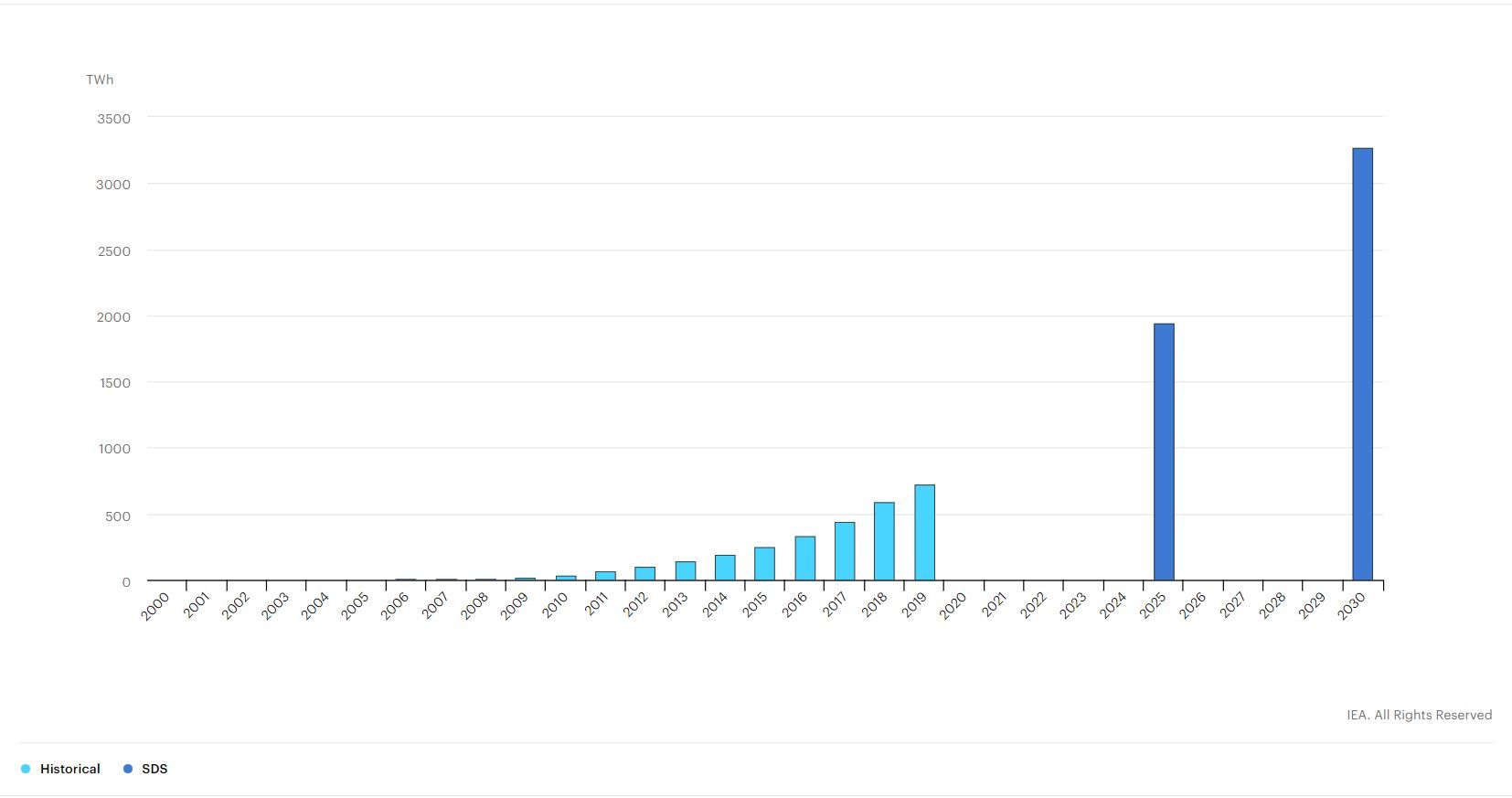
IEA solar PV power generation in the Sustainable Development Scenario, 2000-2030[^7]
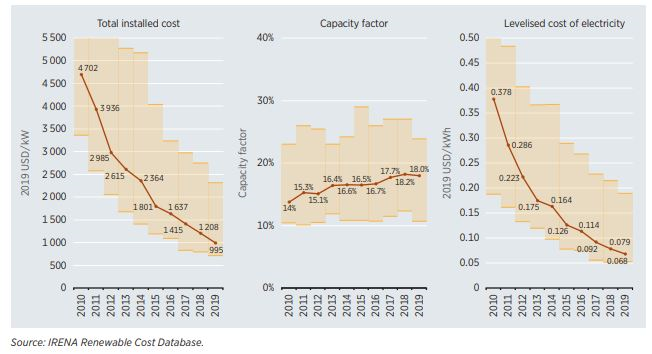
Global weighted average total installed costs, capacity factors and LCOE for PV, 2010–2019
Land use
Solar PV are disposed in lands and most of it on crops category of lands.^5 Because in developed countries, where solar PV are the most deployed, barren lands and desert are scarce (around 10% of the global barren lands surface), it will not be considered in this model. Moreover, only 3% of the urban surface can be used for solar PV, very few rooftops are eligible to solar PV. So for this first version of land use model it will not be considered either.
The power by hectare value has been computed on the base of 357 MWh/acre^6, giving 315059 kWh/ha.
^1: Solar Photovoltaic Technology Basics. NREL.gov, www.nrel.gov/research/re-photovoltaics.html ^2: Capacity factor. NRC.gov, https://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/basic-ref/glossary/capacity-factor-net.html ^3: IEA 2022, World Energy Outlook 2019, IEA, Paris https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2019, License: CC BY 4.0. ^4: IRENA (2020), Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2019, International Renewable Energy Agency, Abu Dhabi. https://www.irena.org/publications/2020/Jun/Renewable-Power-Costs-in-2019 ^5: Scientific report (2021), https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-82042-5 ^6: greenCoast, 2019, Solar Farm Land Requirements: How Much Land Do You Need?, https://greencoast.org/solar-farm-land-requirements/ [^7]: IEA 2022, Solar PV power generation in the Sustainable Development Scenario, 2000-2030, IEA, Paris https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/solar-pv-power-generation-in-the-sustainable-development-scenario-2000-2030, License: CC BY 4.0.