Anaerobic Digestion or Methanization
Introduction: A mixture of methane and carbon dioxide (CO2), biogas can be produced from organic by-products and waste otherwise thrown away or abandoned through anaerobic digestion. Biogas is ideally suited to communities where agricultural residues and animal manure are available as a feedstock. In addition to providing a source of clean energy, anaerobic digestion produces as a by-product a valuable fertiliser that can enhance agricultural production.
How Does an Anaerobic Digester Work? ^6 Anaerobic digestion, or methanization, uses the process of fermentation to break down organic matter from animals. The biomass is heated to approximately 37°C to 38°C (sometimes more than 50°C) and stirred continuously. After at least 20 days and a series of bacteria-induced chemical transformations, the fermented biomass produces biogas . The composition of biogas depends on the type of feedstock and the production pathway. The methane content of biogas typically ranges from 45% to 75% and the carbon dioxyde content from 25% to 55% by volume.
Biogas and biomethane production pathways
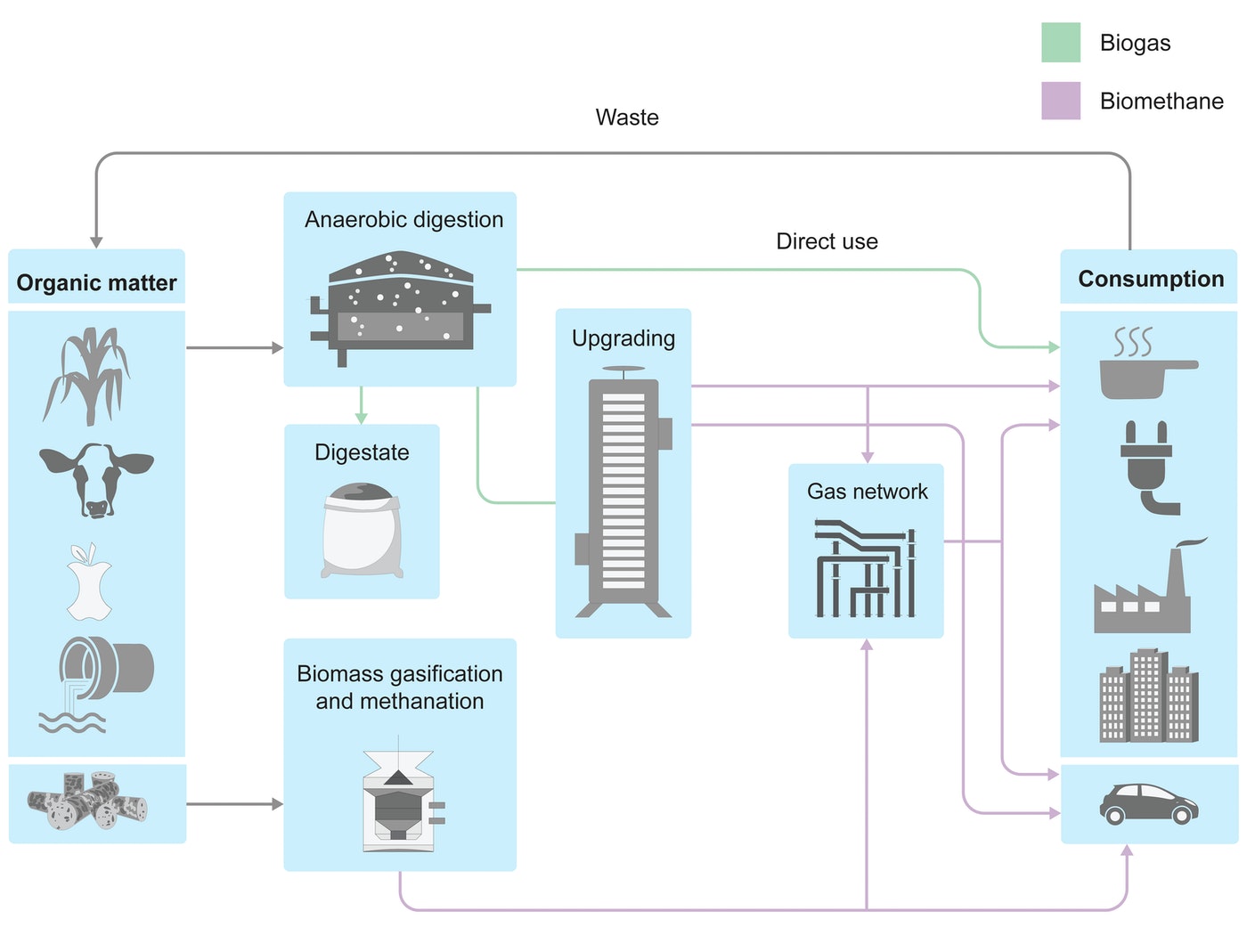 (Image Credit: IEA [^5])
(Image Credit: IEA [^5])
Data
Most of the data used for this model is extracted from the paper of Rajendran & al ^1 which is a review of all papers on anaerobic digestion. World initial production is extracted from the IEA site [^5].
Typical prices of Biogas from anaerobic digestion can be found on IRENA site[^2] : "between USD 0.22 and USD 0.39 per cubic meter of methane for manure-based biogas production, and USD 0.11 to USD 0.50 per cubic meter of methane for industrial waste-based biogas production". This corresponds to a biogas price between 0.02 and 0.078 $/kWh.
The efficiency of the anaerobic digester is mentionned in Carlini & al ^3. The age distribution of biogas plants from anaerobic digestion has been computed with the plant list in ^4.
^1: Rajendran, K. and Murthy, G.S., 2019. Techno-economic and life cycle assessments of anaerobic digestion–A review. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 20, p.101207. [^2]: Biogas Cost Reductions to Boost Sustainable Transport, https://irena.org/newsroom/articles/2017/Mar/Biogas-Cost-Reductions-to-Boost-Sustainable-Transport ^3:Carlini, M., Mosconi, E.M., Castellucci, S., Villarini, M. and Colantoni, A., 2017. An economical evaluation of anaerobic digestion plants fed with organic agro-industrial waste. Energies, 10(8), p.1165. ^4: IEA 2022, http://task37.ieabioenergy.com/plant-list.html, License: CC BY 4.0. [^5]: IEA 2022, Outlook for biogas and biomethane: Prospects for organic growth, https://www.iea.org/reports/outlook-for-biogas-and-biomethane-prospects-for-organic-growth, License: CC BY 4.0.